Glossary of Terms
Air Infiltration Testing
Done to measure the amount of air flow through a window relative to the amount of wind.
Normal testing is based on winds of 25 MPH. Results are shown in cubic feet per minute (Cfm). Remember: When comparing air infiltration tests, lower is better
Air Space
The space between two panes of glass which make up insulated glass
Aluminum Cladding
Extruded aluminum attached to the exterior of a wood window frame & sash to protect the
wood from outside elements. Extruded aluminum (used by Quaker) is much more solid than
roll-form aluminum (used by many other window manufacturers).
Argon Gas
An inert, non-toxic gas placed between insulated glass panes in order to improve the insulating value.
Awning Window
A venting style window whose sash is hinged at the top and when it is opened, the sash cranks out and up. (shown on left)

Block and Tackle Balances
Hardware contained in the window jamb which allows a hung window to operate in an up-anddown manner
Bronze Glass
Produced by adding a colorant to clear glass to give it a bronze tint. Increases protection from sun-exposure and enhances thermal-efficient. It can be used in conjunction with a Low-E coating
Brick Mold
An aluminum exterior trim piece. Normally used with wood windows when they are placed in new buildings that have a brick exterior. Fills gap between the window’s exterior frame and brick for a smoother, more pleasing appearance
BTU
British Thermal Unit. A standard measure for the amount of energy required to raise one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit.
Bulb Weatherstripping
A flexible, hollow, rubber seal used to seal out air/water from the window or door’s interior
Cfm
Cubic feet per minute – a unit of measure used in air infiltration testing, e.g., “maximum .10
Cfm per foot of sash perimeter”
CRF
Condensation Resistance Factor – a measure to show a window’s ability to withstand the
formation of condensation on its glass or main frame. Remember: When comparing CRF,
higher is better.
Capillary Tubes
breathing tubes in serted into butyl spacer of insulated glass, allowing air pressure inside the glass to equalize air pressure outside of glass. This minimizes the possibility of seal failure &/or stress fractures
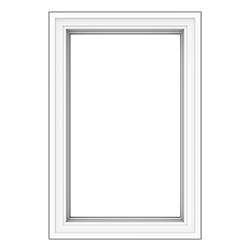
Casement Window
A venting style window whose sash is hinged on the jamb and when it is opened, the sash cranks out and to the right or left. (shown on right)

Condensation
A natural accumulation of water vapor or droplets as the result of warm. Moist air coming in
contact with a cold surface and cooling to its dew point temperature. Condensation may occur when a cold window glass or frame is exposed to humid, indoor air
Conduction
The transfer of heat or cold through a solid material (such as glass or wood) through direct
heat.
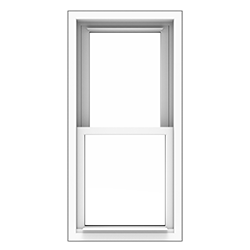
Cottage Style Window
A hung window with two sash which are unequal in size to each other. In a Cottage unit, the
bottom sash is always larger than the top sash
DuraLite®
Butyl sealant used as a spacer between two panes of glass to form insulated glass. This
patented “warm edge” sealant is heat set in an oven and actually adheres itself to the glass.
This minimizes the chance for seal failure (water between the glass). (See application of
DuraLite® in this video: https://youtu.be/BixsQOvQg-k?t=2m35s)
Egress Hardware
Hardware specifically designed so that windows may achieve clear opening size dimensions
that meet fire safety codes.
Egress Window
A window with a minimum clear opening size to allow occupants to escape through the window in case of fire. Egress window sizes are dictated by local fire safety codes.
Emissivity
The relative ability of a surface to reflect or emit heat or radiation. Emissivity factors range from 0.00 to 1.00. The lower the emissivity, the less heat that is emitted through a window system. Emissivity is typically measured by U-Factor (or its opposite, R-Factor).
Energy Star®
Government program created to help consumers easily identify products that save energy, and help protect the environment.

Extruded J-Channel
An addition to vinyl main frame extrusions. Used for new construction homes that have vinyl or metal siding. Covers siding edges where they adjoin the window frame, giving a more pleasing appearance.
Fin Seal Weatherstripping
A fuzzy strip with a hard plastic backing that is used in windows and doors to reduce air
infiltration. Fin Seal Weatherstripping is an upgrade to normal weatherstripping. It has a thin
plastic strip in the middle of the wool pile to further prevent wind infiltration.
Fin Seal Weatherstripping
Allows you to fold a casement window’s the operating crank handle into a concealed position (great for mini-blinds)
Footbolt Lock
Additional locking device used at the sill of a sliding patio door.
Frame Depth
The overall depth of the window or door as measured from the front of the main frame to the
back of the main frame.
Fusion Weld
The overall depth of the window or door as measured from the front of the mai frame to the
back of the main frame.
Grey Glass
Produced by adding a colorant to clear glass to give it a grayish tint. Increases protection from sun-exposure and enhances thermal-efficiency. Very similar to Bronze glass, but slightly more thermally-efficient. Can be used in conjunction with a Low-E coating
Glaze
Glaze or plastic panes, as in a window or skylight. Note that the terms Double-Glazed and
Double-Paned are the same. The term glazed should not be confused with “coated” or “tinted”.
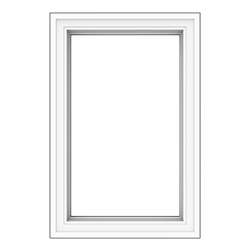
Hopper Window
A venting style window whose sash is hinged at the bottom and when it is opened, the sash cranks out and down. (see image on the right)

Hung Window
Window whose sash operate(s) vertically. Hung windows come in two styles: Single Hung has only one operating sash. Double Hung has two operating sashes.
Inside Snap Trim
Interior finishing trim used to trim a window to the interior wall.
Insulating Foam Wrap
Foam material used around the perimeter of a window during installation. It is used in lieu of or in conjunction with fiberglass insulation.
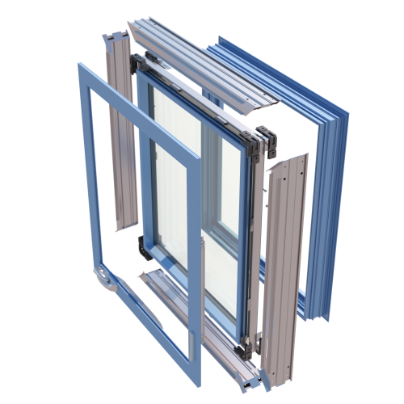
Insulated Glass
Two panes of glass enclosing a hermetically sealed air space. The glass panes are separated by a DuraSeal® spacer to keep the sealed air space free of condensation
Integral Lift Rail
A rail that is an attached part of the sash framing. It is not an added or slider-on piece of
material.
J-Channel
The lip around the exterior perimeter of a window. Siding material is tucked behind it.
Jamb
The vertical side of a window or door frame.
Jamb Extension
A wood or vinyl piece added to the interior or exterior main frame of a window to help it achieve a predetermined frame depth
Jamb Liner
A multi-purpose vinyl liner placed in the left and right jambs of wood clad double hung
windows. provides a protective lining, houses the balance system, allows both sash to slide up and down freely, and increases energy-efficiency
Limited Travel Device
Safety feature that limits the amount a window can open. Because all requests are different,
the amount the window opens or vents must be predetermined when ordered.
Low-E
A microscopically thin, almost invisible metal or metallic oxide layer(s) deposited on a window glazing surface and sealed in an insulated glass unit to reduce the U-Factor by suppressing radiative heat flow through the window. Studies show that it not only keeps heat in during the winter, it also keeps heat out in the summer. It also protects fabrics and wall coverings from fading by blocking harmful U.V. rays.
Main Frame
The outer framing of a window or door that encompasses the sash or door panels.
Mull (or Mullions)
Material or area in which 2 or more windows are joined together.
Mullion Covers
Materials used to cover a joint or joints where two or more windows &/or doors meet.
Muntins
Divider bars which appear to or actually divide a sash into smaller
sections. They can be found within or on a sash, and can be EXTERIOR (outside the glass exterior face), INTERIOR (inside the glass face), INTERNAL (inside the insulating glass airspace), TRUE (dividing the glass), or a combination of these. They are used to enhance the aesthetics of a window door

N.F.R.C
National Fenestration Ratings Council – a non-profit organization created by the window, door & skylight industry. Its primary goal is to provide accurate information to measure and
compare the energy performance of window, door, or skylight products.
Nailing Fin
The part of the window frame that is actually nailed or screwed to a wall or rough opening
frame when a window or door is installed. The nailing fin may be extruded (part of the actual
frame), snapped on, or slid on to the main frame.
Obscure Glass
Also referred to as Frosted Glass, Obscure Glass is nearly opaque. It lets light in yet obscures visibility through the glass. Usually used in private areas such as bathrooms. It should not be confused with One-Way Glass.
Oriel Window
A hung window with two sash which are unequal in size to each other. In an Oriel unit, the top sash is always larger than the bottom sash.
PSF
Pounds per Square Foot – a unit of measure used to test water infiltration through a window or door.
Picture Window/Fixed Window
A window that is not operable
Pocket Depth
Relative to the entire frame depth, it is the measurement from a point in the open window
frame to either the exterior or interior of the open frame. (i.e. 5” frame depth with a 3 1/4”
pocket depth)
Pole Operator
Used to operate windows out of normal reach (such as awning windows up high). Requires
special handles or cranks
Q-Lon Weatherstripping
Protected foam compression sills used to seal our air/water from interior.
Rough Opening
Always expressed as width first, then height. It is the size of the opening needed to correctly
house a window or door.
Rubber Weatherstripping
Flexible rubber seal used to seal out air/water from exterior.
Self-aligning Cam-Type Hardware
A term used to describe a type of sweep lock that allows a window to lock and seal tightly even when it isn’t completely closed (95% or better).
SHGC (Solar Heat Gain Coefficient)
Measures the proportion of solar energy penetrating a building. SHGC is expressed as a value between 0 and 1. Remember: Lower is better when comparing SHGC
Sheet Rock Return Channel
A snap-on material used to house sheet rock and make it flush with the interior face of the
window.
Sill
The horizontal base of a window or door main frame
Snap-in Glazing
Usually a vinyl or aluminum material which holds glass in sash or main frame. Used in lieu of
wrap-around glazing.
Spacer
A material place between 2 or more panes of glass in an insulated glass unit to bond and seal the glazing unit. DuraSeal® is the spacer used in all Quaker windows and doors.
Stainless Street Pivot Bar
Type of pivot bar which connects a sash to the balancing system.
Stick Glazing
Type of glazing (usually wood) which is used to hold glass in the sash or main frame. Used in
lieu of wrap-around glazing.
Tempered Glass
A safety glazing material that provides increased strength and break-resistance. When broken, tempered glass “dies” into fragments the shape of rock salt crystals that eliminate injury
Threshold Ramp
A ramp designed to create a gradual slope from the main frame sill of a door to the interior/
exterior surface.
Tilt latch
Mechanism embedded or attached to a sash which, when operated, allows a sash in a hung
window to tilt-in.
Venting Window
Window whose sash opens by using a cranking mechanism. There are 3 types of venting
windows: Casement, Awning, and Hopper (see images above). They are differentiated by the direction that the sash opens.
Warm edge
A description for a window unit that uses a spacer material (i.e. DuraLite®) to reduce
conductivity between interior and exterior panes of glass. (See application of DuraLite® in this video: https://youtu.be/BixsQOvQg-k?t=2m35s)
Weep Hole
An opening cut into a window sill and or sash rail to allow water to drain to the exterior.
Wrap Around Glazing
Glazing channels which wrap around the glass perimeter. They are used in lieu of stick glazing or snap-in glazing.